Understanding TESE: What Is It and What Are Its Success Rates?
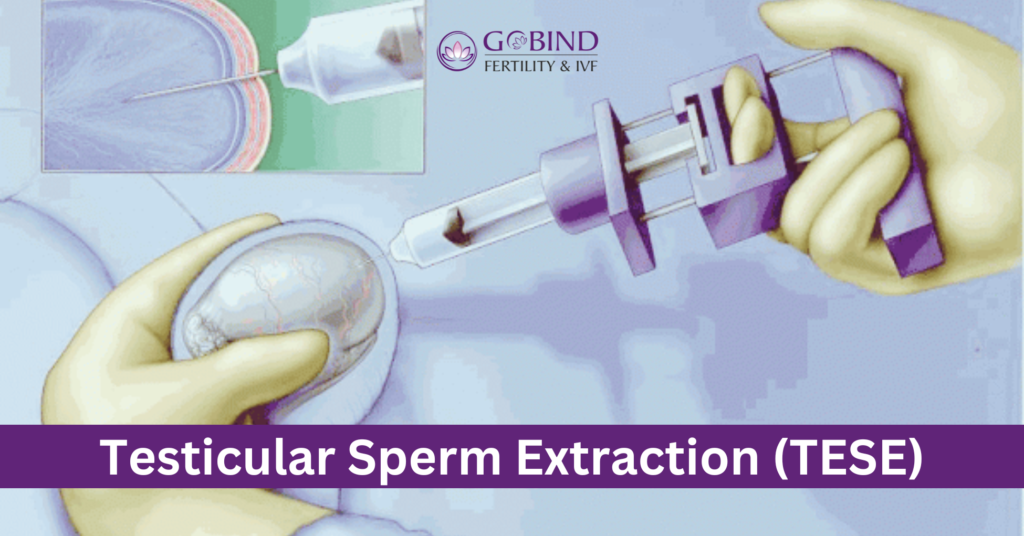
When it comes to addressing male infertility, the landscape of medical treatments has evolved significantly over the years. One advanced procedure that has gathered attention in recent times, is Testicular Sperm Extraction (TESE). If you’re navigating the complexities of fertility treatments, understanding TESE and its success rates can provide valuable insights into your options.
What Is TESE?
Testicular Sperm Extraction (TESE) is a surgical procedure designed to retrieve sperm directly from the testicles. It is typically used in cases where sperm is not present in the ejaculate, a condition known as azoospermia. TESE is often recommended for men with obstructive azoospermia (where there is a blockage in the reproductive tract preventing sperm from being ejaculated) or non-obstructive azoospermia (where there is a failure in sperm production within the testicles).
TESE Procedure
TESE involves a minor surgical operation usually performed under local or general anaesthesia. The process includes:
Anaesthesia: The patient is given anaesthesia to minimize discomfort.
Incision: A small incision is made in the scrotum to access the testicles.
Sperm Retrieval: A small tissue sample is taken from the testicular tissue. This tissue is then examined in the laboratory to find viable sperm.
Closure: The incision is closed with sutures, and the patient is monitored during recovery.
In some cases, a variant known as Micro-TESE is used, which employs a microscope to locate and extract sperm with greater precision, especially in cases where sperm production is severely impaired.
Success Rates of TESE
The success rates of TESE can vary based on several factors, including the underlying cause of azoospermia, the experience of the surgical team, and the patient’s overall health. However, general statistics provide a useful overview:
1 Sperm Retrieval Success Rate: For TESE, the success rate of finding viable sperm ranges from 40% to 60% in cases of non-obstructive azoospermia. This rate can be higher in cases of obstructive azoospermia, often exceeding 80%.
2. Fertility Outcomes: The success of TESE in achieving a pregnancy through assisted reproductive techniques, such as Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI), generally has a good track record. Success rates for achieving pregnancy using sperm retrieved via TESE can be around 30% to 50% per cycle, although this can vary based on the quality of the retrieved sperm and other factors related to the couple’s fertility.
3. Impact of Age and Health: The overall success of TESE also depends on the age and health of the female partner, as well as the overall fertility health of the male partner. Younger female partners and those in good health tend to have better outcomes when combined with TESE.
Conclusion
TESE is a significant advancement in the field of male infertility, providing hope for many men facing challenges with sperm production. With a success rate that varies depending on individual circumstances, it offers a viable option for those seeking to overcome infertility challenges. Consult with one of the best fertility specialists Dr Manju Khurana who can provide a personalized assessment and help you determine the best course of action based on your specific needs and health profile.
As with any medical procedure, understanding your options and working closely with experienced professionals can help you make informed decisions and navigate the path to parenthood with greater confidence.
