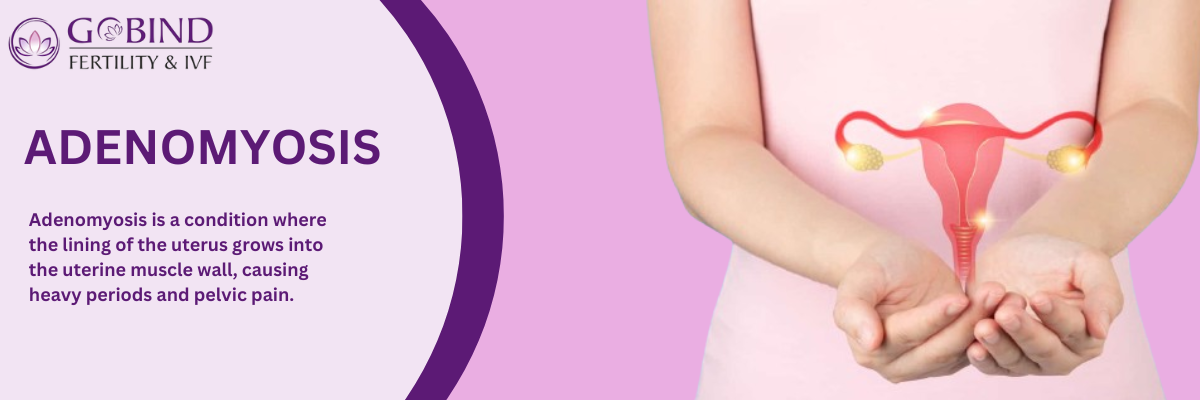
Adenomyosis?
It occurs when the tissue that normally lines the uterus (endometrial tissue) grows into the muscular wall of the uterus.
An abnormal growth of endometrial tissue—the tissue that normally lines the inside of the uterus—into the uterus's muscular wall is known as adenomyosis, a disorder that affects the uterus.
The following are important details regarding adenomyosis:
- Causes: Although the precise cause is uncertain, an excess of estrogen and the invasive development of endometrial cells are thought to be involved.
- Symptoms: Menstrual cramps, persistent pelvic pain, and heavy, painful, protracted periods (dysmenorrhea) are typical signs. In addition, some women report experiencing nausea, bloating, and pain during sexual activity.
- Risk factors: Women with children in their 40s and 50s are most likely to develop adenomyosis. Additionally, people who have had prior uterine surgery or trauma are more prone to experience it.
- Diagnosis: Because the symptoms of adenomyosis might resemble those of other illnesses like endometriosis or uterine fibroids, it is frequently challenging to make a diagnosis. Diagnostic tools that are frequently utilized include magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and transvaginal ultrasound.
- Effect on fertility: Although the exact effect of adenomyosis on fertility is unknown, it may raise the chance of miscarriage or lead to infertility.
- Available treatments: - Hormonal therapies (such as progestins or birth control tablets) and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs) may help control symptoms.
- Treatments such as uterine artery embolization or endometrial ablation can alleviate symptoms.
- When all other therapies fail or the condition is severe, a hysterectomy—the surgical removal of the uterus—is thought to be the only viable option.
Because of severe bleeding and ongoing pelvic pain, adenomyosis can have a very negative influence on a woman's quality of life. It is crucial to receive an early diagnosis and appropriate treatment that is based on the patient's symptoms and future goals for conception.